

YARN Timeline Service v.2 is the next major iteration of Timeline Server, following v.1 and v.1.5. V.2 is created to address two major challenges of v.1.
V.1 is limited to a single instance of writer/reader and storage, and does not scale well beyond small clusters. V.2 uses a more scalable distributed writer architecture and a scalable backend storage.
YARN Timeline Service v.2 separates the collection (writes) of data from serving (reads) of data. It uses distributed collectors, essentially one collector for each YARN application. The readers are separate instances that are dedicated to serving queries via REST API.
YARN Timeline Service v.2 chooses Apache HBase as the primary backing storage, as Apache HBase scales well to a large size while maintaining good response times for reads and writes.
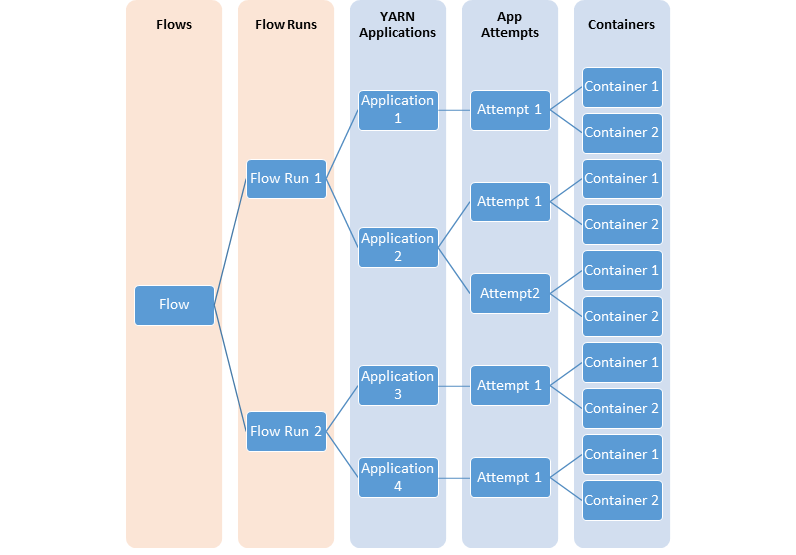
In many cases, users are interested in information at the level of “flows” or logical groups of YARN applications. It is much more common to launch a set or series of YARN applications to complete a logical application. Timeline Service v.2 supports the notion of flows explicitly. In addition, it supports aggregating metrics at the flow level.
Also, information such as configuration and metrics is treated and supported as first-class citizens.
The following diagrams illustrates the relationship between different YARN entities modelling flows.
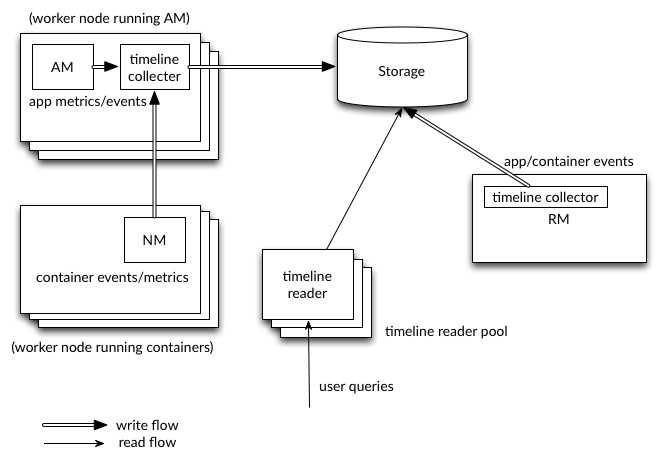
YARN Timeline Service v.2 uses a set of collectors (writers) to write data to the backend storage. The collectors are distributed and co-located with the application masters to which they are dedicated. All data that belong to that application are sent to the application level timeline collectors with the exception of the resource manager timeline collector.
For a given application, the application master can write data for the application to the co-located timeline collectors (which is an NM auxiliary service in this release). In addition, node managers of other nodes that are running the containers for the application also write data to the timeline collector on the node that is running the application master.
The resource manager also maintains its own timeline collector. It emits only YARN-generic lifecycle events to keep its volume of writes reasonable.
The timeline readers are separate daemons separate from the timeline collectors, and they are dedicated to serving queries via REST API.
The following diagram illustrates the design at a high level.
YARN Timeline Service v.2 is currently in alpha (“alpha 1”). It is very much work in progress, and many things can and will change rapidly. Users must enable Timeline Service v.2 only on a test or experimental cluster to test the feature.
Most importantly, security is not enabled. Do not set up or use Timeline Service v.2 until security is implemented if security is a requirement.
A complete end-to-end flow of writes and reads is functional, with Apache HBase as the backend. You should be able to start generating data. When enabled, all YARN-generic events are published as well as YARN system metrics such as CPU and memory. Furthermore, some applications including Distributed Shell and MapReduce can write per-framework data to YARN Timeline Service v.2.
The basic mode of accessing data is via REST. Currently there is no support for command line access. The REST API comes with a good number of useful and flexible query patterns (see below for more information).
The collectors (writers) are currently embedded in the node managers as auxiliary services. The resource manager also has its dedicated in-process collector. The reader is currently a single instance. Currently, it is not possible to write to Timeline Service outside the context of a YARN application (i.e. no off-cluster client).
When YARN Timeline Service v.2 is disabled, one can expect no functional or performance impact on any other existing functionality.
The work to make it truly production-ready continues. Some key items include
New configuration parameters that are introduced with v.2 are marked bold.
| Configuration Property | Description |
|---|---|
| yarn.timeline-service.enabled | Indicate to clients whether Timeline service is enabled or not. If enabled, the TimelineClient library used by applications will post entities and events to the Timeline server. Defaults to false. |
| yarn.timeline-service.version | Indicate what is the current version of the running timeline service. For example, if “yarn.timeline-service.version” is 1.5, and “yarn.timeline-service.enabled” is true, it means the cluster will and must bring up the timeline service v.1.5 (and nothing else). On the client side, if the client uses the same version of timeline service, it must succeed. If the client chooses to use a smaller version in spite of this, then depending on how robust the compatibility story is between versions, the results may vary. Defaults to 1.0f. |
| yarn.timeline-service.writer.class | The class for the backend storage writer. Defaults to HBase storage writer. |
| yarn.timeline-service.reader.class | The class for the backend storage reader. Defaults to HBase storage reader. |
| yarn.system-metrics-publisher.enabled | The setting that controls whether yarn system metrics is published on the Timeline service or not by RM And NM. Defaults to false. |
| Configuration Property | Description |
|---|---|
| yarn.timeline-service.hostname | The hostname of the Timeline service web application. Defaults to 0.0.0.0 |
| yarn.timeline-service.address | Address for the Timeline server to start the RPC server. Defaults to ${yarn.timeline-service.hostname}:10200. |
| yarn.timeline-service.webapp.address | The http address of the Timeline service web application. Defaults to ${yarn.timeline-service.hostname}:8188. |
| yarn.timeline-service.webapp.https.address | The https address of the Timeline service web application. Defaults to ${yarn.timeline-service.hostname}:8190. |
| yarn.timeline-service.writer.flush-interval-seconds | The setting that controls how often the timeline collector flushes the timeline writer. Defaults to 60. |
| yarn.timeline-service.app-collector.linger-period.ms | Time period till which the application collector will be alive in NM, after the application master container finishes. Defaults to 1000 (1 second). |
| yarn.timeline-service.timeline-client.number-of-async-entities-to-merge | Time line V2 client tries to merge these many number of async entities (if available) and then call the REST ATS V2 API to submit. Defaults to 10. |
| yarn.timeline-service.hbase.coprocessor.app-final-value-retention-milliseconds | The setting that controls how long the final value of a metric of a completed app is retained before merging into the flow sum. Defaults to 259200000 (3 days). This should be set in the HBase cluster. |
| yarn.rm.system-metrics-publisher.emit-container-events | The setting that controls whether yarn container metrics is published to the timeline server or not by RM. This configuration setting is for ATS V2. Defaults to false. |
The first part is to set up or pick an Apache HBase cluster to use as the storage cluster. The version of Apache HBase that is supported with Timeline Service v.2 is 1.1.x. The 1.0.x versions do not work with Timeline Service v.2. The 1.2.x versions have not been tested.
Once you have an Apache HBase cluster ready to use for this purpose, perform the following steps.
First, add the timeline service jar to the HBase classpath in all HBase machines in the cluster. It is needed for the coprocessor as well as the schema creator. For example,
cp hadoop-yarn-server-timelineservice-3.0.0-alpha1-SNAPSHOT.jar /usr/hbase/lib/
Then, enable the coprocessor that handles the aggregation. To enable it, add the following entry in region servers’ hbase-site.xml file (generally located in the conf directory) as follows:
<property> <name>hbase.coprocessor.region.classes</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.timelineservice.storage.flow.FlowRunCoprocessor</value> </property>
Restart the region servers and the master to pick up the timeline service jar as well as the config change. In this version, the coprocessor is loaded statically (i.e. system coprocessor) as opposed to a dynamically (table coprocessor).
Finally, run the schema creator tool to create the necessary tables:
bin/hbase org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.timelineservice.storage.TimelineSchemaCreator
The TimelineSchemaCreator tool supports a few options that may come handy especially when you are testing. For example, you can use -skipExistingTable (-s for short) to skip existing tables and continue to create other tables rather than failing the schema creation.
Following are the basic configurations to start Timeline service v.2:
<property> <name>yarn.timeline-service.version</name> <value>2.0f</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.timeline-service.enabled</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> <value>mapreduce_shuffle,timeline_collector</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services.timeline_collector.class</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.timelineservice.collector.PerNodeTimelineCollectorsAuxService</value> </property> <property> <description>The setting that controls whether yarn system metrics is published on the Timeline service or not by RM And NM.</description> <name>yarn.system-metrics-publisher.enabled</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <description>The setting that controls whether yarn container events are published to the timeline service or not by RM. This configuration setting is for ATS V2.</description> <name>yarn.rm.system-metrics-publisher.emit-container-events</name> <value>true</value> </property>
In addition, you may want to set the YARN cluster name to a reasonably unique value in case you are using multiple clusters to store data in the same Apache HBase storage:
<property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id</name> <value>my_research_test_cluster</value> </property>
Also, add the hbase-site.xml configuration file to the client Hadoop cluster configuration so that it can write data to the Apache HBase cluster you are using.
Restart the resource manager as well as the node managers to pick up the new configuration. The collectors start within the resource manager and the node managers in an embedded manner.
The Timeline Service reader is a separate YARN daemon, and it can be started using the following syntax:
$ yarn-daemon.sh start timelinereader
This section is for YARN application developers that want to integrate with Timeline Service v.2.
Developers can continue to use the TimelineClient API to publish per-framework data to the Timeline Service v.2. You only need to instantiate the right type of the client to write to v.2. On the other hand, the entity/object API for v.2 is different than v.1 as the object model is significantly changed. The v.2 timeline entity class is org.apache.hadoop.yarn.api.records.timelineservice.TimelineEntity whereas the v.1 class is org.apache.hadoop.yarn.api.records.timeline.TimelineEntity. The methods on TimelineClient suitable for writing to Timeline Service v.2 are clearly delineated, and they use the v.2 types as arguments.
Timeline Service v.2 putEntities methods come in 2 varieties: putEntities and putEntitiesAsync. The former is a blocking operation which must be used for writing more critical data (e.g. lifecycle events). The latter is a non-blocking operation. Note that neither has a return value.
Creating a TimelineClient for v.2 involves passing in the application id to the factory method.
For example:
// Create and start the Timeline client v.2
TimelineClient client = TimelineClient.createTimelineClient(appId);
client.init(conf);
client.start();
try {
TimelineEntity myEntity = new TimelineEntity();
myEntity.setEntityType("MY_APPLICATION");
myEntity.setEntityId("MyApp1")
// Compose other entity info
// Blocking write
client.putEntities(entity);
TimelineEntity myEntity2 = new TimelineEntity();
// Compose other info
// Non-blocking write
timelineClient.putEntitiesAsync(entity);
} catch (IOException e) {
// Handle the exception
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// In Hadoop 2.6, if attempts submit information to the Timeline Server fail more than the retry limit,
// a RuntimeException will be raised. This may change in future releases, being
// replaced with a IOException that is (or wraps) that which triggered retry failures.
} catch (YarnException e) {
// Handle the exception
} finally {
// Stop the Timeline client
client.stop();
}
As evidenced above, you need to specify the YARN application id to be able to write to the Timeline Service v.2. Note that currently you need to be on the cluster to be able to write to the Timeline Service. For example, an application master or code in the container can write to the Timeline Service, while an off-cluster MapReduce job submitter cannot.
After creating the timeline client, user also needs to set the timeline collector address for the application. If AMRMClient is used then by registering the timeline client by calling AMRMClient#registerTimelineClient is sufficient.
amRMClient.registerTimelineClient(timelineClient);
Else address needs to be retreived from the AM allocate response and need to be set in timeline client explicitly.
timelineClient.setTimelineServiceAddress(response.getCollectorAddr());
You can create and publish your own entities, events, and metrics as with previous versions.
TimelineEntity objects have the following fields to hold timeline data:
Note that when posting timeline metrics, one may choose how each metric should be aggregated through the TimelineMetric#setRealtimeAggregationOp() method. The word “aggregate” here means applying one of the TimelineMetricOperation for a set of entities. Timeline service v2 provides built-in application level aggregation, which means aggregating metrics from different timeline entities within one YARN application. Right now, there are two kinds of operations supported in TimelineMetricOperation:
By default, the NOP operation means not performing any real-time aggregation operation.
Application frameworks must set the “flow context” whenever possible in order to take advantage of the flow support Timeline Service v.2 provides. The flow context consists of the following:
If the flow context is not specified, defaults are supplied for these attributes:
You can provide the flow context via YARN application tags:
ApplicationSubmissionContext appContext = app.getApplicationSubmissionContext();
// set the flow context as YARN application tags
Set<String> tags = new HashSet<>();
tags.add(TimelineUtils.generateFlowNameTag("distributed grep"));
tags.add(Timelineutils.generateFlowVersionTag("3df8b0d6100530080d2e0decf9e528e57c42a90a"));
tags.add(TimelineUtils.generateFlowRunIdTag(System.currentTimeMillis()));
appContext.setApplicationTags(tags);
Querying Timeline Service v.2 is currently only supported via REST API; there is no API client implemented in the YARN libraries.
The v.2 REST API is implemented at under the path, /ws/v2/timeline/ on the Timeline Service web service.
Here is an informal description of the API.
GET /ws/v2/timeline/
Returns a JSON object describing the service instance and version information.
{
"About":"Timeline Reader API",
"timeline-service-version":"3.0.0-alpha1-SNAPSHOT",
"timeline-service-build-version":"3.0.0-alpha1-SNAPSHOT from fb0acd08e6f0b030d82eeb7cbfa5404376313e60 by sjlee source checksum be6cba0e42417d53be16459e1685e7",
"timeline-service-version-built-on":"2016-04-11T23:15Z",
"hadoop-version":"3.0.0-alpha1-SNAPSHOT",
"hadoop-build-version":"3.0.0-alpha1-SNAPSHOT from fb0acd08e6f0b030d82eeb7cbfa5404376313e60 by sjlee source checksum ee968fd0aedcc7384230ee3ca216e790",
"hadoop-version-built-on":"2016-04-11T23:14Z"
}
The following shows the supported queries on the REST API.
With Query Flows API, you can retrieve a list of active flows that had runs most recently. If the REST endpoint without the cluster name is used, the cluster specified by the configuration yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id in yarn-site.xml is taken. If none of the flows match the predicates, an empty list will be returned.
[
{
"metrics": [],
"events": [],
"id": "test-cluster/1460419200000/sjlee@ds-date",
"type": "YARN_FLOW_ACTIVITY",
"createdtime": 0,
"flowruns": [
{
"metrics": [],
"events": [],
"id": "sjlee@ds-date/1460420305659",
"type": "YARN_FLOW_RUN",
"createdtime": 0,
"info": {
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_VERSION": "1",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_RUN_ID": 1460420305659,
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_NAME": "ds-date",
"SYSTEM_INFO_USER": "sjlee"
},
"isrelatedto": {},
"relatesto": {}
},
{
"metrics": [],
"events": [],
"id": "sjlee@ds-date/1460420587974",
"type": "YARN_FLOW_RUN",
"createdtime": 0,
"info": {
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_VERSION": "1",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_RUN_ID": 1460420587974,
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_NAME": "ds-date",
"SYSTEM_INFO_USER": "sjlee"
},
"isrelatedto": {},
"relatesto": {}
}
],
"info": {
"SYSTEM_INFO_CLUSTER": "test-cluster",
"UID": "test-cluster!sjlee!ds-date",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_NAME": "ds-date",
"SYSTEM_INFO_DATE": 1460419200000,
"SYSTEM_INFO_USER": "sjlee"
},
"isrelatedto": {},
"relatesto": {}
}
]
With Query Flow Runs API, you can drill further down to get the runs (specific instances) of a given flow. This returns the most recent runs that belong to the given flow. If the REST endpoint without the cluster name is used, the cluster specified by the configuration yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id in yarn-site.xml is taken. If none of the flow runs match the predicates, an empty list will be returned.
GET /ws/v2/timeline/clusters/{cluster name}/users/{user name}/flows/{flow name}/runs/
or
GET /ws/v2/timeline/users/{user name}/flows/{flow name}/runs/
[
{
"metrics": [],
"events": [],
"id": "sjlee@ds-date/1460420587974",
"type": "YARN_FLOW_RUN",
"createdtime": 1460420587974,
"info": {
"UID": "test-cluster!sjlee!ds-date!1460420587974",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_RUN_ID": 1460420587974,
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_NAME": "ds-date",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_RUN_END_TIME": 1460420595198,
"SYSTEM_INFO_USER": "sjlee"
},
"isrelatedto": {},
"relatesto": {}
},
{
"metrics": [],
"events": [],
"id": "sjlee@ds-date/1460420305659",
"type": "YARN_FLOW_RUN",
"createdtime": 1460420305659,
"info": {
"UID": "test-cluster!sjlee!ds-date!1460420305659",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_RUN_ID": 1460420305659,
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_NAME": "ds-date",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_RUN_END_TIME": 1460420311966,
"SYSTEM_INFO_USER": "sjlee"
},
"isrelatedto": {},
"relatesto": {}
}
]
With this API, you can query a specific flow run identified by cluster, user, flow name and run id. If the REST endpoint without the cluster name is used, the cluster specified by the configuration yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id in yarn-site.xml is taken. Metrics are returned by default while querying individual flow runs.
GET /ws/v2/timeline/clusters/{cluster name}/users/{user name}/flows/{flow name}/runs/{run id}
or
GET /ws/v2/timeline/users/{user name}/flows/{flow name}/runs/{run id}
{
"metrics": [
{
"type": "SINGLE_VALUE",
"id": "org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormatCounter:BYTES_READ",
"aggregationOp": "NOP",
"values": {
"1465246377261": 118
}
},
{
"type": "SINGLE_VALUE",
"id": "org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormatCounter:BYTES_WRITTEN",
"aggregationOp": "NOP",
"values": {
"1465246377261": 97
}
}
],
"events": [],
"id": "varun@QuasiMonteCarlo/1465246348599",
"type": "YARN_FLOW_RUN",
"createdtime": 1465246348599,
"isrelatedto": {},
"info": {
"UID":"yarn-cluster!varun!QuasiMonteCarlo!1465246348599",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_RUN_END_TIME":1465246378051,
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_NAME":"QuasiMonteCarlo",
"SYSTEM_INFO_USER":"varun",
"SYSTEM_INFO_FLOW_RUN_ID":1465246348599
},
"relatesto": {}
}
With this API, you can query all the YARN applications that are part of a specific flow. If the REST endpoint without the cluster name is used, the cluster specified by the configuration yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id in yarn-site.xml is taken. If the number of matching applications are more than the limit, the most recent apps up to the limit will be returned. If none of the apps match the predicates, an empty list will be returned.
GET /ws/v2/timeline/clusters/{cluster name}/users/{user name}/flows/{flow name}/apps
or
GET /ws/v2/timeline/users/{user name}/flows/{flow name}/apps
[
{
"metrics": [ ],
"events": [ ],
"type": "YARN_APPLICATION",
"id": "application_1465246237936_0001",
"createdtime": 1465246348599,
"isrelatedto": { },
"configs": { },
"info": {
"UID": "yarn-cluster!application_1465246237936_0001"
},
"relatesto": { }
},
{
"metrics": [ ],
"events": [ ],
"type": "YARN_APPLICATION",
"id": "application_1464983628730_0005",
"createdtime": 1465033881959,
"isrelatedto": { },
"configs": { },
"info": {
"UID": "yarn-cluster!application_1464983628730_0005"
},
"relatesto": { }
}
]
With this API, you can query all the YARN applications that are part of a specific flow run. If the REST endpoint without the cluster name is used, the cluster specified by the configuration yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id in yarn-site.xml is taken. If number of matching applications are more than the limit, the most recent apps up to the limit will be returned. If none of the apps match the predicates, an empty list will be returned.
GET /ws/v2/timeline/clusters/{cluster name}/users/{user name}/flows/{flow name}/runs/{run id}/apps
or
GET /ws/v2/timeline/users/{user name}/flows/{flow name}/runs/{run id}/apps/
[
{
"metrics": [],
"events": [],
"id": "application_1460419579913_0002",
"type": "YARN_APPLICATION",
"createdtime": 1460419580171,
"info": {
"UID": "test-cluster!sjlee!ds-date!1460419580171!application_1460419579913_0002"
},
"configs": {},
"isrelatedto": {},
"relatesto": {}
}
]
With this API, you can query a single YARN application identified by the cluster and the application ID. If the REST endpoint without the cluster name is used, the cluster specified by the configuration yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id in yarn-site.xml is taken. Flow context information i.e. user, flow name and run id are not mandatory but if specified in query param can preclude the need for an additional operation to fetch flow context information based on cluster and app id.
GET /ws/v2/timeline/clusters/{cluster name}/apps/{app id}
or
GET /ws/v2/timeline/apps/{app id}
{
"metrics": [],
"events": [],
"id": "application_1460419579913_0002",
"type": "YARN_APPLICATION",
"createdtime": 1460419580171,
"info": {
"UID": "test-cluster!sjlee!ds-date!1460419580171!application_1460419579913_0002"
},
"configs": {},
"isrelatedto": {},
"relatesto": {}
}
With this API, you can query generic entities identified by cluster ID, application ID and per-framework entity type. If the REST endpoint without the cluster name is used, the cluster specified by the configuration yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id in yarn-site.xml is taken. Flow context information i.e. user, flow name and run id are not mandatory but if specified in query param can preclude the need for an additional operation to fetch flow context information based on cluster and app id. If number of matching entities are more than the limit, the most recent entities up to the limit will be returned. This endpoint can be used to query containers, application attempts or any other generic entity which clients put into the backend. For instance, we can query containers by specifying entity type as YARN_CONTAINER and application attempts by specifying entity type as YARN_APPLICATION_ATTEMPT. If none of the entities match the predicates, an empty list will be returned.
GET /ws/v2/timeline/clusters/{cluster name}/apps/{app id}/entities/{entity type}
or
GET /ws/v2/timeline/apps/{app id}/entities/{entity type}
[
{
"metrics": [ ],
"events": [ ],
"type": "YARN_APPLICATION_ATTEMPT",
"id": "appattempt_1465246237936_0001_000001",
"createdtime": 1465246358873,
"isrelatedto": { },
"configs": { },
"info": {
"UID": "yarn-cluster!application_1465246237936_0001!YARN_APPLICATION_ATTEMPT!appattempt_1465246237936_0001_000001"
},
"relatesto": { }
},
{
"metrics": [ ],
"events": [ ],
"type": "YARN_APPLICATION_ATTEMPT",
"id": "appattempt_1465246237936_0001_000002",
"createdtime": 1465246359045,
"isrelatedto": { },
"configs": { },
"info": {
"UID": "yarn-cluster!application_1465246237936_0001!YARN_APPLICATION_ATTEMPT!appattempt_1465246237936_0001_000002"
},
"relatesto": { }
}
]
With this API, you can query a specific generic entity identified by cluster ID, application ID, per-framework entity type and entity ID. If the REST endpoint without the cluster name is used, the cluster specified by the configuration yarn.resourcemanager.cluster-id in yarn-site.xml is taken. Flow context information i.e. user, flow name and run id are not mandatory but if specified in query param can preclude the need for an additional operation to fetch flow context information based on cluster and app id. This endpoint can be used to query a single container, application attempt or any other generic entity which clients put into the backend. For instance, we can query a specific YARN container by specifying entity type as YARN_CONTAINER and giving entity ID as container ID. Similarly, application attempt can be queried by specifying entity type as YARN_APPLICATION_ATTEMPT and entity ID being the application attempt ID.
GET /ws/v2/timeline/clusters/{cluster name}/apps/{app id}/entities/{entity type}/{entity id}
or
GET /ws/v2/timeline/apps/{app id}/entities/{entity type}/{entity id}
{
"metrics": [ ],
"events": [ ],
"type": "YARN_APPLICATION_ATTEMPT",
"id": "appattempt_1465246237936_0001_000001",
"createdtime": 1465246358873,
"isrelatedto": { },
"configs": { },
"info": {
"UID": "yarn-cluster!application_1465246237936_0001!YARN_APPLICATION_ATTEMPT!appattempt_1465246237936_0001_000001"
},
"relatesto": { }
}